Setting up Port Forwarding
Getting Started
Here are some things you need to prepare for setting up Port Forwarding:
- Have access to your router / modem
- Some ISP block access to your device
- Write down the admin user and password of the router / modem
- Typically, this is located on the device itself or the user manual
- Have a smart phone or tablet and install Fing
What Do you do Next?
You need to find the following IPs:
- ISP’s WAN IP Address
- Router’s LAN IP Address
- Controller’s LAN IP Address
Download and install Fing on your smart phone or tablet. Follow these steps for iOS:
- Open the App and connect to your wireless Network
- On this screen, you will see your Controller’s IP under the device name

- Then Click on Network tab in the bottom

- Then Click on your Network on the Top

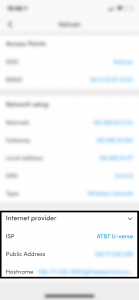
- Finally Scroll down to get your WAN IP, which is called Public Address
- In this last screen, your Gateway (Router’s IP) will be shown
- You must navigate to your Router’s IP address
- Login using the credentials you wrote down
Now for the most difficult part
We need to add a Firewall Rule or as some router’s call it an Application Rule or Port Map Rule. To do this we need to know which port the Controller uses.
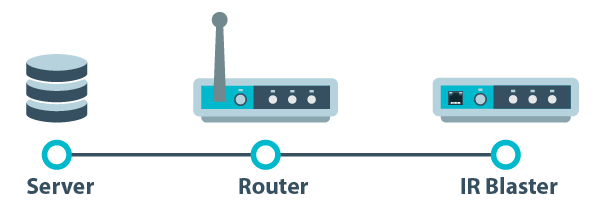
There is no one solution for setting up Port Forwarding. Why is that? Everyone manufacture has a slightly different way of doing this and has slightly different terms; some may call it port mapping others might say application rule. Look at your router’s manual and or talk to your Internet System Provider (ISP) to see if they can help. There is no one solution to this. Even though this is no one solution, the Port Forwarding rule will be the same, just about:
- Global Cache (Port 4998 is for IR) #1
- External Port Range
- Start 4998 or 9999 or 6777 or anything really
- End 4998 or 9999 or 6777 or anything really
- Internal Port Range
- Start 4998
- End 4998
- Destination IP
- Local IP, such as 192.168.10.35
- External Port Range
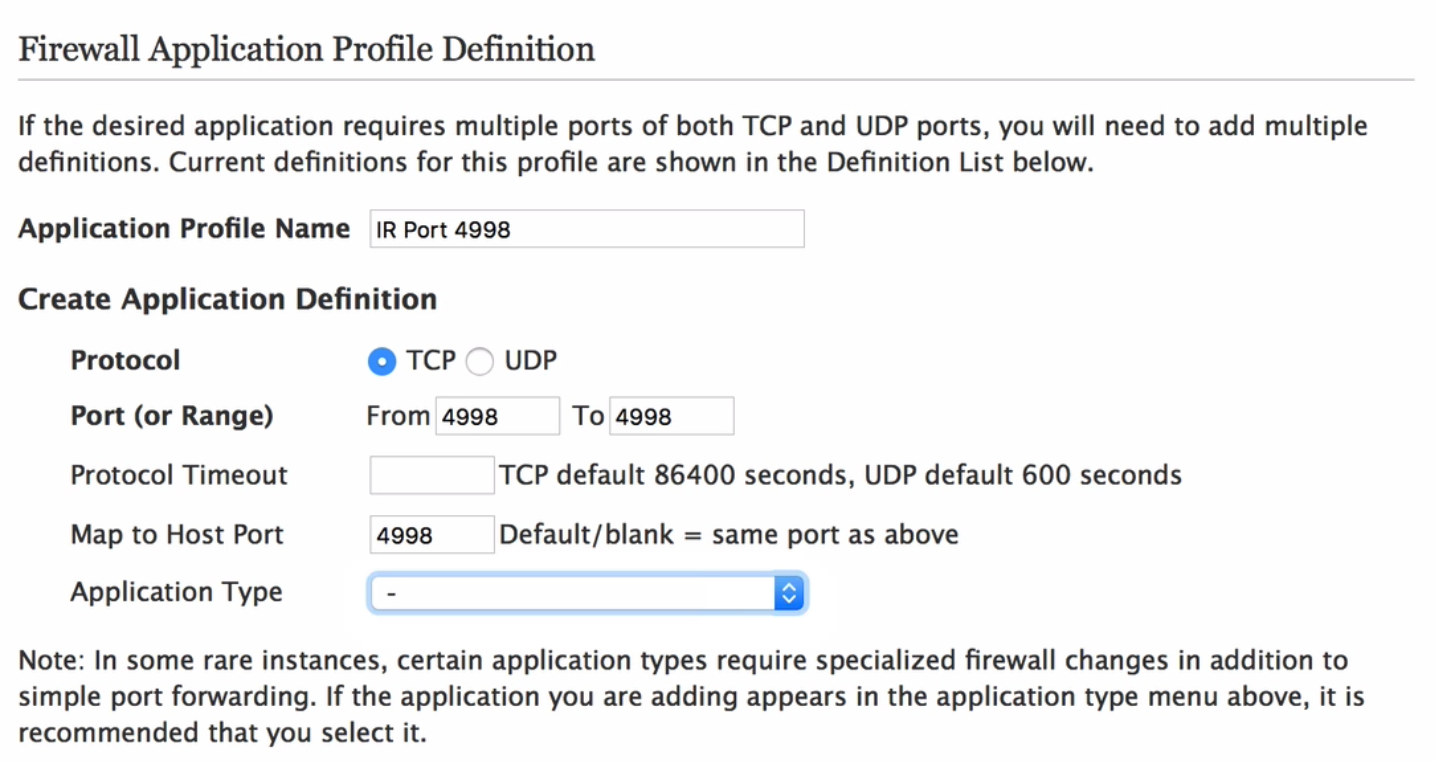
The External Port Range is the port on your Router and it can be anything. Typically you would keep the port the same as the internal port, but it doesn’t have to be. The Internal Port Range is fixed and known per controller. This means that the internal port range will never change and always be the same.
Can I do Port Forwarding for two controllers?
Yes, you just have to change the external port range. Here is an example for a second controller:
- Global Cache (Port 4998 is for IR) #2
- External Port Range
- Start 6777
- End 6777
- Internal Port Range
- Start 4998
- End 4998
- Destination IP
- Local IP, such as 192.168.10.36
- External Port Range
Notice how the only thing that change was the Start and End Port Range, and of course the destination ip of course.
2 Replies to “Setting up Port Forwarding”
Comments are closed.